一、基本情况
环境污染控制与修复科技创新团队于2015年组建而成。目前,团队成员由12名从事环境科学与工程研究的教师组成,其中,教授3名、副教授2名、讲师7名;拥有博士学位10人,硕士学位2人;入选湖南省121创新人才工程第三层次1人,衡阳市青年科技人才2人,公司“拔尖人才”计划2人。主要开展农田-农作物重金属污染防治以及水体污染修复研究。团队成员已承担国家自然科学基金项目5项,湖南省自然科学基金项目10 项,湖南省教育厅重点项目1项,优秀青年项目2项,各类科研经费累计500余万元;发表学术论文50余篇,其中SCI、EI收录30余篇,获得2019年度湖南省自然科学奖三等奖1项。
二、研究方向
1. 农作物重金属污染防治
2. 土壤污染修复
3. 废水无害化处理
三、团队负责人
辛俊亮:男,博士,教授,主要从事环境污染控制与修复方面的研究工作。2010年6月毕业于中山大学环境科学专业,获博士学位,同年引进到edf186壴定发娱乐官网工作。2014年4月至2015年4月由国家留学基金委公派美国加州大学伯克利分校进行访问研究。目前是湖南省121创新人才工程第三层次、衡阳市青年科技人才、edf186壴定发娱乐官网“拔尖人才”、环境科学与工程学科带头人。已主持国家自然科学基金项目2项,湖南省自然科学基金项目4项;以第一作者或通讯作者在《Plant and Soil》、《Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry》等SCI源刊发表论文20余篇。
四、团队成员
黄白飞:女,1983年生,教授,中山大学生态学博士,衡阳市青年科技人才、环境工程专业学术带头人、edf186壴定发娱乐官网“拔尖人才”,主要从事环境生物学与污染生态学研究。
周立:男,1967年生,教授,中南大学化学工艺博士,主要从事冶金废水处理研究。
黄樱樱:女,1991年生,副教授,中山大学生态学博士,主要从事农作物重金属污染防治。
申创:男,1990年生,讲师,中山大学生态学博士,主要从事土壤重金属污染治理。
杨丽:男,1980年生,讲师,南开大学环境科学博士,实验中心主任,主要从事工业污水深度处理研究。
付惠玲:女,1992年生,讲师,中山大学生态学博士,主要从事农作物重金属污染防治研究。
廖琼:女,1992年生,讲师,湖南农业大学植物营养学博士,主要从事农作物重金属污染防治研究。
王蓓:女,1992年生,讲师,湖南大学环境科学与工程博士,主要从事污水处理研究。
曹攀:男,1991年生,讲师,中南大学冶金物理化学博士,主要从事冶金废水处理研究。
李大军:男,1979年生,副教授,贵州大学环境工程硕士,主要从事工业废水无害化处理研究。
周唯:女,1989年生,讲师,湖南大学环境科学与工程硕士,主要从事重金属废水处理研究。
五、主要研究成果
1. 明确了作物品种间根系吸收转运镉的能力和可食部分镉含量差异形成的关系
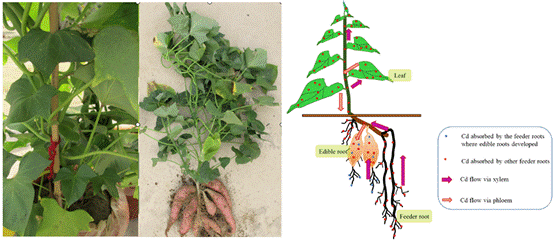
开展了辣椒、甘薯、茄子品种间镉积累差异的研究,筛选出了一批镉积累能力稳定的低镉和高镉品种。发现辣椒果实镉含量与根系吸收镉的能力无关,而与根-茎叶间以及茎叶-果实间镉的转运能力有关。通过分析甘薯体内镉的转运,提出了甘薯块根镉可能源于茎叶和着生于块根的细根输送。
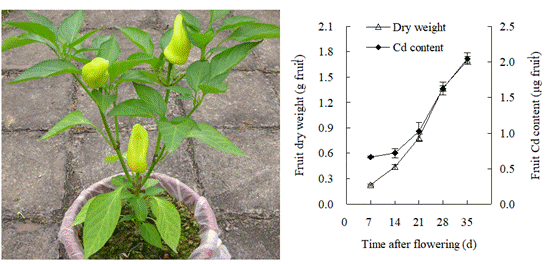
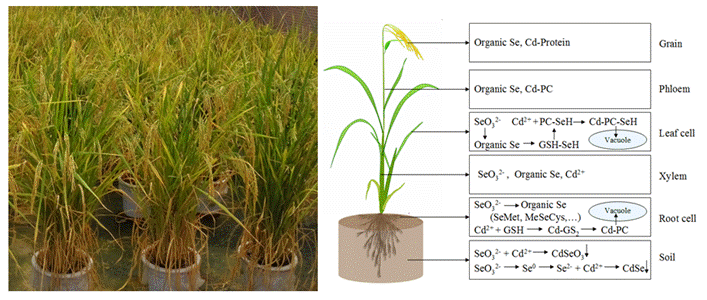
通过杂交获得了低镉高产的水稻杂交一代,证明了水稻低镉积累的特性是可稳定遗传的,传统的“三系杂交”培育高产低镉杂交水稻品种是可行的。发现硒可以显著减少水稻吸收镉,降低镉从茎叶向糙米转运;镉主要是影响水稻对硒的吸收,但并不影响体内硒的转运。
2. 阐明了辣椒体内镉的分配以及根系形态和根系分泌物对品种间镉吸收转运差异的影响机理
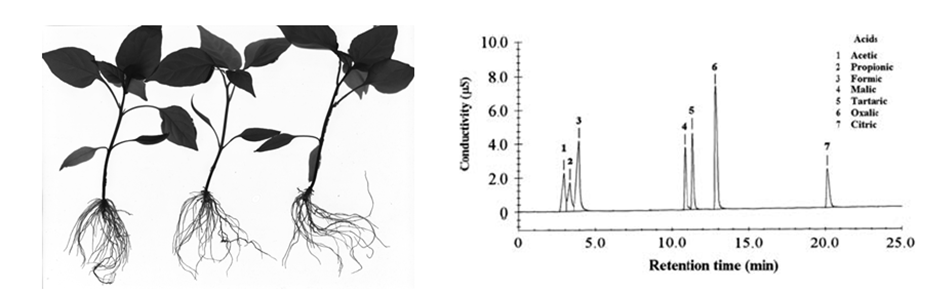
通过分析镉的亚细胞分布和化学形态后发现,辣椒根系液泡是区隔化镉的主要细胞器,而在茎、叶和果实中细胞壁是固定镉的主要细胞器。低镉辣椒品种根系固定镉的能力更强,减少了镉向地上部转运;而高镉品种茎叶中可移动性镉的浓度较低镉品种高,这有利于镉向果实转运。此外,发现高镉与低镉辣椒品种在根系形态方面有明显差异,与高镉品种相比,低镉品种根尖数较少,根长较短,根表面积较小;而根长、根表面积和根尖数与茎叶镉含量和根茎间镉的转运效率显著正相关。特别是,根尖凯氏带不完整而且侧根形成会破坏根原基附近凯氏带的完整性,这有利于镉通过质外体途径从凯氏带破损处进入中柱继而向地上部转运。我们还发现高、低镉辣椒品种根际可交换态镉含量并无明显差异,这可能与它们根系吸收镉的能力类似有关。低镉品种根系分泌的低分子量有机酸总量与高镉品种也无差异;然而,低分子量有机酸的组成与镉胁迫强度和品种有关。
3. 解析了作物可食部分镉的来源及品种间差异形成的生理机制
通过分根法和高、低镉品种间相互嫁接法研究了甘薯块根中镉的来源和块根镉含量品种间差异形成的原因。结果发现,甘薯块根中的镉来源于茎叶和细根的输送,品种间块根镉积累的差异不仅与镉从细根向块根转运有关,而且也与细根向茎叶转运有关。

通过对辣椒全生长期的跟踪试验首次发现,辣椒果实镉浓度随着生长时间的延长而降低,即嫩辣椒镉浓度高于老辣椒。高镉辣椒品种从根向茎叶转运镉的能力更强,转运速度也更快。辣椒品种间果实镉含量差异的形成也与茎叶通过韧皮部向果实转运镉的能力有关。

4. 发现了可以显著降低农作物积累镉的土壤改良剂
通过多次试验表明,合理施用农家肥、粉煤灰、硼肥、钾肥、硒肥不仅可以明显降低土壤有效镉含量,改善土壤质量,而且可以增加农产品产量,降低根系吸收镉能力,提高营养价值。
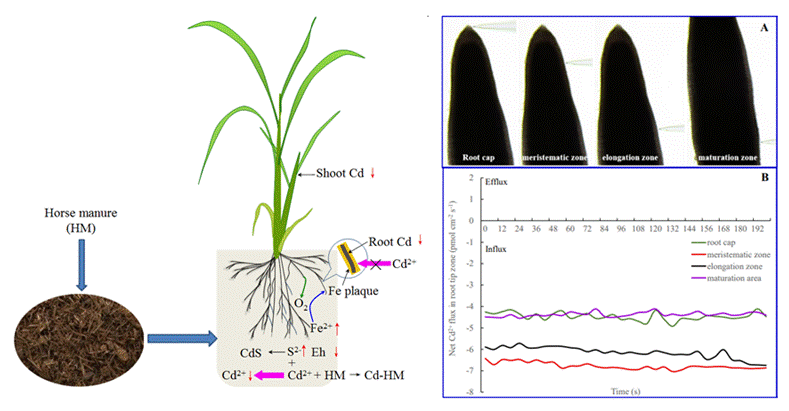
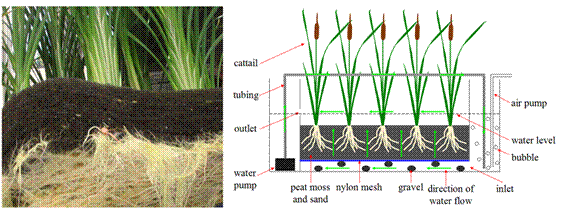
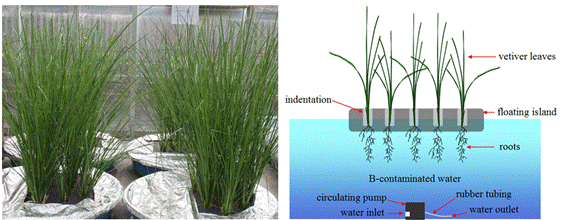
5.筛选到了一种超积累硼的香根草生态型,发现了浮岛处理硼污水的可持续性优于人工湿地
比较了香蒲、芦苇和香根草吸收、转运、积累硼的能力;发现了一种可以超积累硼的香根草生态型Sierra;系统分析了上行流香蒲-人工湿地和香蒲-浮岛处理硼污染废水的效率。
已发表的相关论文:
1. Chuang Shen, Hui-Ling Fu, Qiong Liao, Bai-Fei Huang, Ying-Ying Huang*, Jun-Liang Xin*. Selection for low-cadmium cultivars and cadmium subcellular distribution comparison between two selected cultivars of eggplant (Solanum melongena L.). Environ Sci Pollut Res DOI: 10.1007/s11356-021-14652-5
2. Aiguo Yin, Baifei Huang, Jiayi Xie, Yingying Huang, Chuang Shen, Junliang Xin*. Boron decreases cadmium influx into root cells of Capsicum annuum by altering cell wall components and plasmalemma permeability. Environ Sci Pollut Res DOI: 10.1007/s11356-021-14441-0
3. Aiguo Yin, Chuang Shen, Yingying Huang, Maofeng Yue, Baifei Huang, Junliang Xin*. Reduction of Cd accumulation in Se-biofortified rice by using fermented manure and fly ash. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2020, 27: 39391-39401
4. Lang Yang, Li Fan, Baifei Huang, Junliang Xin*. Efficiency and mechanisms of fermented horse manure, vermicompost, bamboo biochar, and fly ash on Cd accumulation in rice. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2020, 27: 27859-27869
5. Wei Zhou*, Wenqing Tang, Junliang Xin. Functionalization of xonotlite composite with amidoxime groups for the sorption of Cu (II) ion. Water Air Soil Pollut 2020, 231: 406
6. Wei Zhou*, Junliang Xin, Wenqing Tang. Investigation of Pb (II) and Cd (II) removal from aqueous solution by organic-modified xonotlite. Int J Environ Analyt Chem 2020, DOI: 10.1080/03067319.2020.1838492
7. Baifei Huang*, Hongwen Dai, Wenjing Zhou, Lijing Peng, Meizhen Li, Renjie Wan, Wenting He. Characteristics of Cd accumulation and distribution in two sweet potato cultivars. Int J Phytoremediat 2019, 21(4): 391-398
8. Junliang Xin*, Baifei Huang. Comparison of boron uptake and translocation in two vetiver genotypes and evaluation of boron removal efficiency of vetiver floating islands. Int J Phytoremediat 2018, 20(8): 847-854
9. Dajun Li, Li Zhou*. Adsorption of heavy metal tolerance strains to Pb2+ and Cd2+ in wastewater. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2018, 25: 32156-32162
10. Baifei Huang, Junliang Xin*, Hongwen Dai, Wenjing Zhou. Effects of interaction between cadmium (Cd) and selenium (Se) on grain yield and Cd and Se accumulation in a hybrid rice (Oryza sativa) system. J Agric Food Chem 2017, 65(43): 9537-9546
11. Junliang Xin*, Baifei Huang. Comparison of boron uptake, translocation, and accumulation in reed, cattail, and vetiver: an extremely boron-tolerant plant, vetiver. Plant Soil 2017, 416(1-2): 17–25
12. Junliang Xin, Hongwen Dai, Baifei Huang*. Assessing the roles of roots and shoots in the accumulation of cadmium in two sweet potato cultivars using split-root and reciprocal grafting systems. Plant Soil 2017, 412: 413-424
13. Junliang Xin*, Baifei Huang. Effects of pH on boron accumulation in cattail (Typha latifolia) shoots, and evaluation of floating islands and upward flow mesocosms for the removal of boron from wastewater. Plant Soil 2017, 412: 163-176
14. Junliang Xin, Baifei Huang*, Hongwen Dai, Yangxiu Mu. Characterization of root morphology and root-derived low molecular weight organic acids in two sweet potato cultivars exposed to cadmium. Arch Agron Soil Sci 2017, 63(5): 723-734
15. Hongwen Dai, Xiuxian Song, Baifei Huang, Junliang Xin*. Health risks of heavy metals to the general public in Hengyang, China, via consumption of rice. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 2016, 22(8): 1636-1650
16. Junliang Xin, Baifei Huang*, Hongwen Dai. Difference in root-to-shoot Cd translocation and characterization of Cd accumulation during fruit development in two Capsicum annuum cultivars. Plant Soil 2015, 394: 287-300
17. Baifei Huang, Junliang Xin*, Hongwen Dai, Wenjing Zhou, Lijing Peng. Identification of low-Cd cultivars of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.) after growing on Cd-contaminated soil: uptake and partitioning to the edible roots. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22: 11813-11821
18. Junliang Xin, Baifei Huang*, Hongwen Dai, Wenjing Zhou, Yumei Yi, Lijing Peng. Roles of rhizosphere and root-derived organic acids in Cd accumulation by two hot pepper cultivars. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22: 6254-6261
19. Baifei Huang, Junliang Xin*, Hongwen Dai, Aiqun Liu, Wenjing Zhou, Yumei Yi, Kebing Liao. Root morphological responses of three hot pepper cultivars to Cd exposure and their correlations with Cd accumulation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22: 1151–1159
20. Baifei Huang, Junliang Xin*, Hongwen Dai, Aiqun Liu, Wenjing Zhou, Kebing Liao. Translocation analysis and safety assessment in two water spinach cultivars with distinctive shoot Cd and Pb concentrations. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21: 11565–11571
21. Junliang Xin, Baifei Huang*, Hongwen Dai, Aiqun Liu, Wenjing Zhou, Kebing Liao. Characterization of cadmium uptake, translocation and distribution in young seedlings of two hot pepper cultivars that differ in fruit cadmium concentration. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21: 7449-7456
22. Junliang Xin, Baifei Huang*. Subcellular distribution and chemical forms of cadmium in two hot pepper cultivars differing in cadmium accumulation. J Agric Food Chem 2014, 62(2): 508-515
23. Junliang Xin, Baifei Huang*, Aiqun Liu, Wenjing Zhou, Kebing Liao. Identification of hot pepper cultivars containing low Cd levels after growing on contaminated soil: uptake and redistribution to the edible plant parts. Plant Soil 2013, 373: 415-425
24. Junliang Xin, Baifei Huang, Zhongyi Yang*, Jiangang Yuan, Yadong Zhang. Comparison of cadmium subcellular distribution in different organs of two water spinach (Ipomoea aquatica Forsk.) cultivars. Plant Soil 2013, 372: 431–444
25. Junliang Xin, Baifei Huang, Junzhi Yang, Zhongyi Yang*, Jiangang Yuan, Yangxiu Mu. Role of roots in cadmium accumulation of two water spinach cultivars: reciprocal grafting and histochemical experiments. Plant Soil 2013, 366: 425-432